Binary Representation of Characters
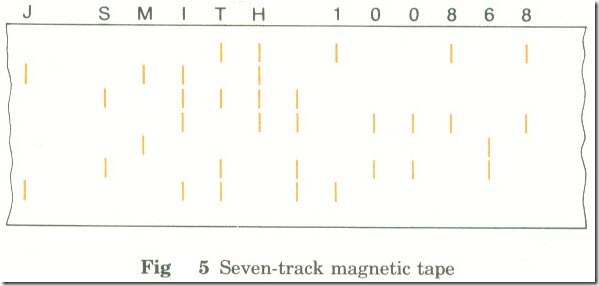
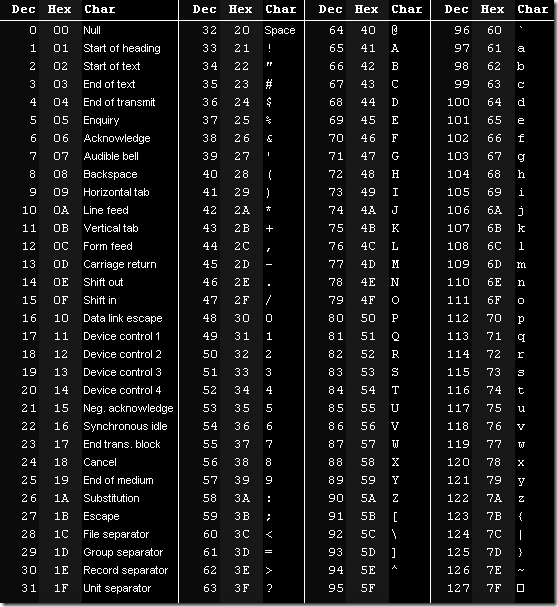
Binary Representation of Characters When characters are transmitted or stored each character is represented as a binary string. The number of bits used to represent each character differs from one system to another. On punched cards there were 12 hole positions for each character, and on some paper tapes there were only 5. In most modern systems, seven, eight or nine bits are used. In general the number of different characters which can be encoded is 2 n , where n is the number of bits used for each character. e.g. The number of different characters you can have with an eight-bit code is 2 8 = 256. Worked question Eight-bit storage locations are used to store coded characters. One bit is a parity bit. 0000 0000 and 1111 1111 both have special uses and cannot be used to code characters. How many different characters can be represented? Seven bits are used for the actual code. Seven bits gives 2 7 = 128 characters. Two codes cannot be used No. of possible characters =...